
It includes instance-wide metadata such as logon accounts, endpoints, linked servers, and system configuration settings. Master: master database stores all system level information for an instance of SQL Server.
They are used by SSMS and other SQL Server APIs and tools, so it is not recommended to modify the system databases manually. System databases are created automatically when SQL Server is installed. There are two types of databases in SQL Server: System Database and User Database. SQL Server Management Studio is widely used to work with a SQL Server database. A login is used to gain access to a SQL Server instance and a database user is used to access a database. SQL Server databases are stored in the file system as files. Each instance of SQL Server can have one or more databases. In SQL Server, a database is made up of a collection of objects like tables, functions, stored procedures, views etc. SQL Server - Stored Procedure Parameters.SQL Server - GRANT/REVOKE Permissions to User.Or you could specify the data and log file locations when creating your database, a good habit that everyone should have! I still prefer to set the default values, in order to help those that might not have good habits formed yet. You will find the option for this on the ‘Database Engine Configuration’ screen as follows:īy doing this during the installation you can avoid the need to restart the service at a later date to make this simple change. I’d suggest that you configure these directories when you are installing SQL Server. Run that, restart the instance, and then run our create database script again. , N'SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer'ĮXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE' In fact, after you make your change in the SSMS, hit the little button at the top that says ‘Script’ and check out what is being done behind the scenes: EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE' The reason why is because the default locations are read from registry values. Turns out that setting the default database locations requires you to restart the SQL instance in order for those changes to take effect. Press OK, and we’ll run our create database script again (don’t forget to drop the original database first) to find this result set:
#Create db in sql server management studio update#
Let’s update the setting to point to the new directories: It’s also important to note that storing your data and log files on the same disk is not a recommended practice. These changes will only apply to new databases created from this point forward. It is important to note that updating these locations will NOT migrate the current data and log files to the new directories.
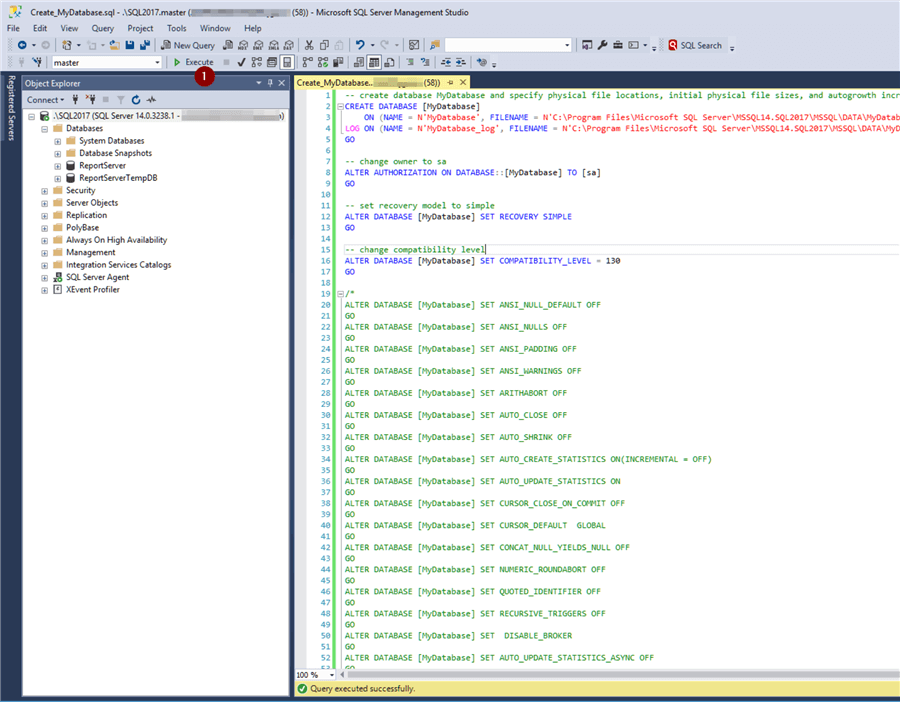
I will create two new folders (C:SQLData and C:SQLLogs) to store the data and log files for new databases. Which returns the locations of our data and log files, which we see are the defaults:Ĭhanging the default is easy enough, we can just update the file locations inside of SSMS. If we create a simple database we can verify that the files are written to these directories: CREATE DATABASE TestFileLoc You can see these properties for yourself by right-clicking on the instance name inside of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and navigating to the ‘Database Settings’ tab: When you create a database in SQL Server and do not specify a file location for your data and log files SQL Server will rely on the default locations as defined in the server properties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
